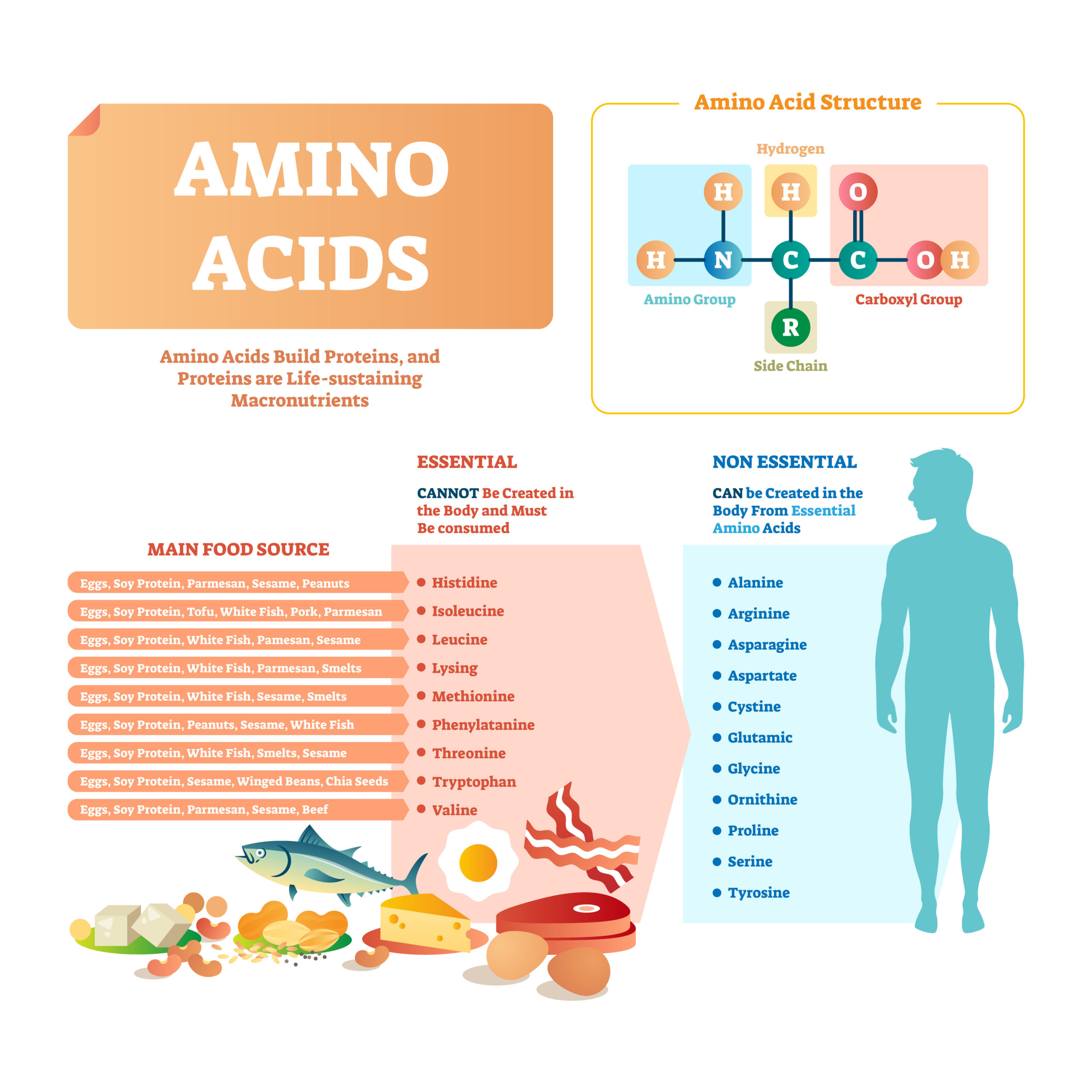
Genes and Nutrition
Each of us is metabolically unique. Gene variations known as SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) often are a factor in an individual’s ability to metabolize or use nutrients efficiently. Each of our specific nutrient needs is affected by which specific combination of SNPs we have, but with thousands known to impact nutrition metabolism, how do we know what those needs are?
NRI researchers are working to create a “catalog” of SNPs that alter our nutritional needs by understanding how genetic and other complex biological information can be used to better estimate individual nutrition requirements and intolerances. Our scientists use bioinformatics to extract such information from population and intervention studies, develop rules for predicting individual needs, and bring precision nutrition to health care providers and consumers with digital tools.
Publications
Genes and Nutrition Publications
2020
Genetic variants affecting bone mineral density and bone mineral content at multiple skeletal sites in Hispanic children. Voruganti VS
Precision (Personalized) Nutrition: Understanding Metabolic Heterogeneity. Zeisel S
2019
DNA methylation in mice is influenced by genetics as well as sex and life experience. French J
Cytosolic 10-formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase regulates glycine metabolism in mouse liver. Krupenko S
Deleterious mutations in ALDH1L2 suggest a novel cause for neuro-ichthyotic syndrome. Krupenko S
Fine mapping and identification of serum urate loci in American Indians: The Strong Heart Family Study. Voruganti VS
Heterogeneity in Metabolic Responses to Dietary Fructose. Voruganti VS
Genetic analysis of hsCRP in American Indians: The Strong Heart Family Study. Voruganti VS
A trans-ancestral meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies reveals loci associated with childhood obesity. Voruganti VS
Healthy dietary patterns and risk and survival of breast cancer: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Voruganti VS
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Genome-Wide Interaction Analyses Reveal DPP10-Pulmonary Function Association. Voruganti VS
2018
C16-ceramide is a natural regulatory ligand of p53 in cellular stress response. Krupenko N
Nutritional Genomics of Cardiovascular Disease. Voruganti VS
Genetic determinants of BMI from early childhood to adolescence: the Santiago Longitudinal Study. Voruganti VS
Serum Lipid Concentrations and FADS Genetic Variants in Young Mexican College Students: The UP-AMIGOS Cohort Study. Voruganti VS
Arsenic-gene interactions and beta-cell function in the Strong Heart Family Study. Voruganti VS
Dietary Modulation of the Epigenome. Zeisel S
2017
Exome sequencing reveals novel genetic loci influencing obesity-related traits in Hispanic children. Voruganti VS
Genetic variation underlying renal uric acid excretion in Hispanic children: the Viva La Familia Study. Voruganti VS
Reduced brain volume and impaired memory in betaine homocysteine S-methyltransferase knockout mice. Zeisel S
Choline, Other Methyl-Donors and Epigenetics. Zeisel S
2016
CerS6 Is a Novel Transcriptional Target of p53 Protein Activated by Non-genotoxic Stress. Krupenko N
Genotype, B-vitamin status, and androgens affect spaceflight-induced ophthalmic changes. Zeisel S
Related News
Nutrition Training for Young Doctors Lacks Bite
October 25, 2017 – Most US medical schools do not require medical students to learn basic nutrition theory, even though poor diet is the leading preventable risk factor for disability or early death in the United States. “It takes at least 25-30 hours of medical school instruction to achieve just basic nutrition competencies,”
Build Stronger Muscles with All Kinds of Protein
August 28, 2017 – From the desks of Martin Kohlmeier, MD, PhD and Robyn Amos-Kroohs, PhD
Protein is an important part of every cell in the body. Protein is also a building block of enzymes, hormones, and other important substances used in body processes. It’s a major component of most body systems, including the immune system, metabolism, and circulatory system. Its importance is why protein is known as a macronutrient, meaning that large amounts are required to help the body function appropriately on a daily basis. And unlike sugar and fats, macronutrients that have acquired bad reputations, protein is recognized as an important part of a healthy diet.
Visiting Scholar's Research Assists Development of Training Program
August 25, 2016 • The Nutrition Research Institute (NRI) welcomes visiting scholar Rodrigo San Cristobal from the Universidad de Navarra in Pamplona, Spain, who is working with NRI faculty member Martin Kohlmeier, M.D., Ph.D., to develop a certification program in nutrigenetics for licensed healthcare professionals.
The “-omics” of Nutrient Metabolism
July 1, 2015 • How our bodies use the nutrients that nourish us drives much of the science at the Nutrition Research Institute. Recent advances in nutrition studies have shed light on the metabolic fates of nutrients and about the molecular actors and mechanisms responsible for the underlying processes. A major reason for the explosive advances in the understanding of nutrient metabolism has been the massive investigative use of all kinds of “-omics,” new fields of study for the mining of data-rich biological information.
ISNN congress to expand the evidence base for genome-directed personal nutrition
May 11, 2015 • The 9th Congress of the International Society of Nutrigenetics and Nutrigenomics (ISNN) presents “Expanding the Evidence Base for Genome-directed Personal Nutrition.”
Training Your Doctor in Nutrition
April 6, 2015 • We rely on our physicians to heal us when we are ill, but more and more, we are needing a trained reliable source of sound nutritional advice when it comes to preventing illness or getting healthy after disease strikes. Until recently most medical doctors in this country were barely trained in the science of human nutrition.